In an era where protecting sensitive health information is paramount, the NHSmail Secure Email Standard plays a crucial role in safeguarding data within the UK’s healthcare system. Managed by NHS Digital, the DHCB1596 standard ensures that emails exchanged between NHS organizations, as well as with other accredited public sector bodies, comply with stringent security protocols.
By adhering to the Data Protection Act 2018 and GDPR, the secure email service enhances patient confidentiality while enabling seamless communication across healthcare providers.
The DHCB1596 Controls are a very healthy cybersecurity controls to mantain on an organization regardless if you need certification with the NHS .
This post has been made to help and ensure you mantain and configure a Email/Security- Basic EDR healthy tenant for enabling reslicence towards cyber attacks following the DHCB1596 Guidelines . The post also includes how to implement 94 Cyber resilence checks to improve your CIS 365 Benchmark and Secure Score
Included Controls
- Healthy Secure email controls
- Healthy office365 hardening settings ( Cis 365 bechmark )
- Review of Mailfow rules , spam & spoof rules in Exchange 365
Additional Tools & Security Upgrades
- Consider implementing an advanced BEC solution ( Ironscales, Proof point , Avananan , Mimecast )
- Consider implementing an additional MDR/EDR advanced solution ( huntress, Malware Bytes MDR, Sentinel one , Crowdstrike )
- Consider having strong BYOD policies
- Consider performing Phishing simulations regularly to train your users
- Embrace Zero trust & Assume breach methodology
- Consider cybersecurity an enabler to do things securely and not “block” things
- Consider SIEM solutions when viable ( implement SOAR and automate as much as possible)
- Consider reviewing and avoiding Alert fatigue
- Consider implementing playbooks for different attacks
- Consider implementing security coding practices
- Consider implementing Network segmentation to stop lateral movement
- Consider implementing Dark web monitoring tools for your passwords & breaches
- Consider data masking techniques for sensitive information in development or non-production environments
- Consider doing data anonymization when possible
- Review your Data retention policies to avoid risk of exposure of unessesary data
- Implement Risk management policies for cybersecurity resilence & identify risky areas or systems
- Review BCP plans and perform excercises ( simulations ) assesing risk overall your deparments .
- Ensure to perform 2 anual pentests a year ( Internal/External )
- Do not forget about Vulnerability management ( You have to patch it ! )
- Know your data to be able to protect your data ( implement classification and encryption and DLP policies )
- Consider a form of threat ingelligence & Training for your IT teams or processes
- Condifering implementing an additional Webfiltering solution ( DNS filter, Web titan , Cisco Umbrella & infoblox )
- Considering writting Security Policies at management level to mantain the requirements on this post
- Consider mantaining cybersecurity certifications for your company for security continuity
- Look possible financial positive outcomes ( bringing cybersecurity could mean bringing costumers that value your cyber posture as company ) . Cybersecurity does not have to be something that is not an enabler or cant bring cash flow
- Consider reviewing your cyber insurance at least 1 a year
- Consider using Password managers in IT teams and other main teams
- Consider adhering to Data laws in order to drawn your strategies
- Consider having frameworks into adquiring new solutions and softwares ( Shadow IT policy )
- Remember that awareness is one of the best defenses, interact with your end users and stakeholders regularly to implement a cybersecurity mindset
- Consider mantaining a database with all your applications , systems and data maps following ITIL pratices & ensuring all changes fo through Change control process .
- Consider mantaining access control lists of administrators on all your platforms and review them regularly
- Consider having a third party cybersecurity expert company to assit you in case of a cyber security incident
- Consider having incident/response plans based on application & Risk
- Consider evaluating your third party risk as part of your cyber security strategy
Recommended Antispam/Anti Phishing controls 365 tenant
- Implement Security Standard policy or Strict Policy for antispam / Antiphishing
https://digital.nhs.uk/services/nhsmail/the-secure-email-standard
Healthy Secure email controls * DMARC policy
Anti-spoofing – DMARC Policy review
- Review your Anti Spoofing and dmarc policy . Set DMARC policy to P=Reject policy
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) is an essential tool for protecting your domain from email spoofing. It helps external organizations determine how to handle emails that appear to be spoofing your domain, particularly as part of the NHS Secure Email Standard. DMARC policies can be customized using the ‘p’ tag within a DNS TXT record. There are three primary options:
- P=none: No action is taken on spoofed emails, making this an ideal initial setup.
- P=quarantine: Spoofed emails are moved to the recipient’s junk folder, a recommended step before full rejection.
- P=reject: Spoofed emails are rejected outright, which is the strongest form of protection but should be implemented gradually after monitoring.
It’s recommended to start with a “p=none” policy to monitor email traffic and then progressively move to “p=quarantine” or “p=reject” to prevent unauthorized use of your domain
Protection from Spoofing: DMARC helps prevent attackers from sending emails that appear to come from your domain, which can be used for phishing attacks, fraud, or spreading malware. By setting a DMARC policy, you reduce the risk of your organization’s reputation being compromised through spoofed emails.
Improving Email Deliverability: When your domain is protected by DMARC, email recipients (e.g., external organizations) are more likely to trust emails from your domain. This increases the likelihood that legitimate emails are delivered successfully, avoiding junk or spam folders.
Monitoring and Reporting: DMARC provides detailed reports on who is sending emails from your domain, allowing you to track potential misuse or unauthorized attempts. This visibility helps you identify vulnerabilities before fully enforcing strict policies like “reject.”
DKIM policy – ensuring all domains are signed
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email authentication method that allows the receiving mail server to check if an email claiming to be from your domain was indeed sent and authorized by you. It uses cryptographic signatures that are added to the email headers. Here’s why it’s essential to configure DKIM:
- Email Security: DKIM helps to prevent email spoofing, phishing, and fraud by verifying the sender’s domain and ensuring that the message was not altered during transmission.
- Improve Email Deliverability: Emails from a domain without DKIM are more likely to be marked as spam or rejected by other email servers, especially as more email providers prioritize secure email practices.
- Brand Protection: By ensuring your domain’s reputation is not used in spoofing or phishing attacks, you protect your brand and its trustworthiness.
365 Domain SKIM Signing
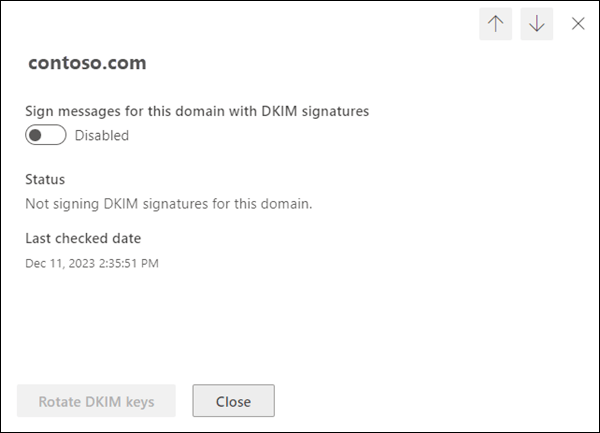
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-office-365/email-authentication-dkim-configure
Review your Antiphishing/Spam Policies

- Make a good use of the preset security policies ( It is better to use standard/strict policies when able ) This configurations are auto-managed by microsoft
- Review all your rules + policies for spam and phishing. Ensure no additional rules allowing senders or ips are created instead whitelist senders using reporting tool on the microsoft blades managing the allow/block list instead of creating exceptions in Anti-spam policies
- Make sure you create internal processes to whitelist sender using “Reporting tool and the tenant /allow list ” and do not encourage to whitelist using spam/phishing policies
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-office-365/tenant-allow-block-list-about
Use the configuration analyser and analyse your security configuration drive

The dashboard provides an overview of your current security posture by calculating a score based on your configuration, behavior, and controls across Microsoft 365.
It breaks down different security areas, such as identity protection, data protection, device management, and email security (which includes DKIM and other email-related protections).
review your Defender EDR Blade configuartion
Enhance your organization’s security posture using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Configuration in defender blade.

Tamper Protection – Prevents disabling of key security features.Automatically Resolve Alerts – Reduces alert fatigue by auto-resolving threats.Restrict Correlation to Scoped Device Groups – Focuses alerts by device group.Hide Potential Duplicate Device Records – Cleans up the device inventory.Custom Network Indicators – Controls traffic to specific domains or IPs.Web Content Filtering – Blocks harmful websites.Live Response – Enables remote investigation of devices.Device Discovery – Detects unmanaged devices on your network.Unified Audit Log – Logs all audited actions for compliance.
CIS 365 bechmarks recommended settings
CIS (Account / Authentication and Azure Active Directory
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 1.1.1 (L1) Ensure Security Defaults is disabled | Go to Azure AD > Properties and ensure Security Defaults is disabled to avoid unnecessary security defaults. |
| 1.1.2 (L1) Ensure MFA is enabled for admin roles | Navigate to Azure AD > Conditional Access and create a policy to enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all administrative roles. |
| 1.1.3 (L1) Ensure sign-in frequency is enabled for admin users | In Azure AD > Conditional Access, configure Sign-in frequency settings for administrative users to ensure sessions are regularly re-authenticated. |
| 1.1.4 (L1) Ensure MFA is enabled for all users | Create a Conditional Access Policy in Azure AD to require MFA for all users in the organization. |
| 1.1.5 (L1) Ensure Microsoft Authenticator is configured to protect against MFA fatigue | In Azure AD > MFA settings, configure the Microsoft Authenticator app and enable protections against repeated MFA prompts. |
| 1.1.6 (L2) Ensure phishing-resistant MFA strength is required for administrators | Use FIDO2 security keys or Certificate-based MFA in Conditional Access policies to enable phishing-resistant MFA for administrators. |
| 1.1.7 (L1) Ensure between two and four global admins are designated | Go to Azure AD > Roles and administrators and ensure that only 2-4 global administrators are assigned to minimize security risks. |
| 1.1.8 (L1) Ensure self-service password reset is enabled | Enable Self-Service Password Reset by going to Azure AD > Password Reset and allowing users to reset their passwords securely. |
| 1.1.9 (L1) Ensure custom banned passwords list is used | Configure a custom banned passwords list in Azure AD > Security > Authentication methods > Password protection to prevent common passwords. |
| 1.1.10 (L1) Ensure password protection is enabled for on-prem Active Directory | Enable password protection for hybrid environments via Azure AD Connect, applying protections to on-prem AD. |
| 1.1.11 (L1) Enable Conditional Access policies to block legacy authentication | In Azure AD > Conditional Access, create a policy that blocks older, less secure authentication methods (e.g., IMAP, POP). |
| 1.1.12 (L1) Ensure password hash sync is enabled for hybrid deployments | In Azure AD Connect, ensure Password Hash Synchronization is enabled to sync passwords securely for hybrid environments. |
| 1.1.13 (L2) Enable Azure AD Identity Protection sign-in risk policies | Enable Sign-in risk policies in Azure AD > Identity Protection to mitigate risks from unusual or suspicious sign-ins. |
| 1.1.14 (L2) Enable Azure AD Identity Protection user risk policies | Configure User risk policies in Azure AD > Identity Protection to take automated actions (e.g., MFA or password reset) when user risk is high. |
| 1.1.15 (L2) Ensure Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is used to manage roles | Go to Azure AD > Privileged Identity Management to configure time-bound and audit-based management of privileged roles. |
| 1.1.16 (L2) Ensure only managed/approved public groups exist | Audit public groups in Azure AD > Groups and restrict membership or creation to managed, organizationally approved groups. |
| 1.1.17 (L2) Ensure collaboration invitations are sent to allowed domains only | Restrict external collaboration in Azure AD > External Collaboration Settings to specific, approved domains. |
| 1.1.18 (L2) Ensure LinkedIn account connections are disabled | In Azure AD > User Settings > LinkedIn account connections, disable the setting to prevent LinkedIn profile sharing with organizational data. |
| 1.1.19 (L2) Ensure ‘Remain signed in’ option is hidden | In Azure AD > Company Branding, configure the option to hide “Keep me signed in” prompts during login. |
CIS (Data Management)
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 3.1 (L2) Ensure the customer lockbox feature is enabled | Go to Microsoft 365 Admin Center > Settings > Services & Add-ins, enable the Customer Lockbox feature to control Microsoft support access to your data. |
| 3.2 (L2) Ensure SharePoint Online Information Protection policies are set up and used | In SharePoint Admin Center, set up Information Protection policies by configuring Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies to protect sensitive data. |
| 3.3 (L2) Ensure ‘External access’ is restricted in the Teams admin center | In Teams Admin Center, configure external access settings to only allow collaboration with trusted domains or disable external access entirely. |
| 3.4 (L1) Ensure DLP policies are enabled | In Microsoft 365 Compliance Center, enable Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies to prevent sensitive information from being shared or leaked. |
| 3.5 (L1) Ensure DLP policies are enabled for Microsoft Teams | Go to Microsoft 365 Compliance Center, and configure DLP policies for Microsoft Teams to prevent the sharing of sensitive information. |
| 3.6 (L2) Ensure that SharePoint guest users cannot share items they don’t own | In SharePoint Admin Center > Sharing Settings, configure policies that prevent guest users from sharing files or items they don’t own. |
| 3.7 (L2) Ensure external file sharing in Teams is enabled for only approved cloud storage services | In Teams Admin Center, limit external file sharing to approved cloud storage services like OneDrive and SharePoint, blocking others. |
CIS (Email Security / Exchange Online)
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 4.1 (L1) Ensure the Common Attachment Types Filter is enabled | In Exchange Admin Center > Mail Flow > Rules, enable the Common Attachment Types Filter to block potentially dangerous attachments (e.g., .exe, .bat). |
| 4.2 (L1) Ensure Exchange Online Spam Policies are set to notify administrators | Go to Exchange Admin Center > Protection > Spam filter, and configure the spam filter policy to notify administrators when spam is detected. |
| 4.3 (L1) Ensure all forms of mail forwarding are blocked and/or disabled | In Exchange Admin Center > Mail Flow, create a rule to block or disable all types of automatic mail forwarding to external domains. |
| 4.4 (L1) Ensure mail transport rules do not whitelist specific domains | Review Mail Flow Rules in Exchange Admin Center and ensure that no specific domains are whitelisted, which could expose your organization to phishing. |
| 4.5 (L2) Ensure Safe Attachments policy is enabled | In Microsoft Defender for Office 365, enable the Safe Attachments policy to scan all incoming attachments for malware. |
| 4.6 (L1) Ensure that an anti-phishing policy has been created | Create an anti-phishing policy in Microsoft Defender for Office 365 to protect against email spoofing and phishing attacks. |
| 4.7 (L1) Ensure that DKIM is enabled for all Exchange Online domains | In Exchange Admin Center, enable DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to digitally sign emails and prevent email spoofing. |
| 4.8 (L1) Ensure that SPF records are published for all Exchange Domains | Ensure that Sender Policy Framework (SPF) DNS records are correctly published for all Exchange domains to help detect email spoofing. |
| 4.9 (L1) Ensure DMARC Records for all Exchange Online domains are published | Publish Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) records for your domains to improve email authentication. |
| 4.10 (L1) Ensure notifications for internal users sending malware is Enabled | Configure malware detection policies in Exchange Admin Center to notify administrators when internal users send malware-infected emails. |
| 4.11 (L2) Ensure MailTips are enabled for end users | In Exchange Admin Center > Mail Flow, enable MailTips to provide users with helpful tips about potential issues when sending emails (e.g., external recipients, large attachments). |
| 4.12 (L1) Ensure Priority account protection is enabled and configured | In Microsoft Defender for Office 365, enable Priority Account Protection to apply enhanced security to high-risk users (e.g., executives). |
| 4.13 (L1) Ensure Priority accounts have ‘Strict protection’ presets applied | Go to Microsoft Defender for Office 365 > Safe Attachments / Safe Links policies and apply strict protection presets to Priority Accounts. |
CIS (Auditing)
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 5.1.1 (L1) Ensure ‘Access reviews’ for Guest Users are configured | In Azure AD > Identity Governance > Access Reviews, configure access reviews specifically for Guest Users to periodically review their access permissions. |
| 5.1.2 (L1) Ensure ‘Access reviews’ for high privileged Azure AD roles are configured | Set up access reviews for privileged roles in Azure AD > Identity Governance > Access Reviews to periodically check that only authorized users have admin privileges. |
| 5.2 (L1) Ensure Microsoft 365 audit log search is enabled | In Microsoft 365 Compliance Center > Audit Log, ensure Audit Log Search is enabled to track user and admin activities for security reviews. |
| 5.3 (L1) Ensure mailbox auditing for all users is enabled | In Exchange Admin Center, enable Mailbox Auditing to track and log actions taken in users’ mailboxes for security and compliance purposes. |
| 5.4 (L1) Ensure the Azure AD ‘Risky sign-ins’ report is reviewed at least weekly | Go to Azure AD > Security > Identity Protection, and regularly review the Risky Sign-ins report to identify compromised accounts. |
| 5.5 (L1) Ensure the Application Usage report is reviewed at least weekly | In Microsoft 365 Admin Center > Reports > Usage, review the Application Usage report weekly to monitor trends and detect unusual app usage. |
| 5.6 (L1) Ensure the self-service password reset activity report is reviewed at least weekly | Go to Azure AD > Reports > Password Reset Activity, and review the Self-Service Password Reset report weekly for any unusual password resets. |
| 5.7 (L1) Ensure user role group changes are reviewed at least weekly | Regularly review Azure AD > Audit Logs for any changes to user role groups, ensuring no unauthorized modifications were made. |
| 5.8 (L1) Ensure mail forwarding rules are reviewed at least weekly | In Exchange Admin Center > Mail Flow, regularly review mail forwarding rules to ensure no unauthorized forwarding has been set up. |
| 5.9 (L1) Ensure all security threats in the Threat protection status report are reviewed at least weekly | In Microsoft Defender for Office 365, review the Threat Protection Status Report weekly to monitor and address security threats. |
| 5.10 (L1) Ensure the Account Provisioning Activity report is reviewed at least weekly | In Azure AD > Audit Logs, review Account Provisioning Activity to ensure proper account setup and catch any anomalies in new account creation. |
| 5.11 (L1) Ensure non-global administrator role group assignments are reviewed at least weekly | Review non-global administrator roles in Azure AD > Roles and administrators to ensure the correct users have appropriate access. |
| 5.12 (L1) Ensure the spoofed domains report is reviewed weekly | In Microsoft Defender for Office 365 > Reports, review the Spoofed Domains report to catch and mitigate domain impersonation attempts. |
| 5.13 (L2) Ensure Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is enabled and configured | Go to Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps and ensure it’s configured to monitor and protect access to cloud applications. |
| 5.14 (L1) Ensure the ‘Restricted entities’ report is reviewed weekly | In Microsoft 365 Compliance Center, review the Restricted Entities report to identify entities with limited permissions or access. |
| 5.15 (L1) Ensure Guest Users are reviewed at least biweekly | Perform biweekly reviews of Guest Users in Azure AD > Users, ensuring they only have necessary and legitimate access to resources. |
CIS (Storage)
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 6.1 (L2) Ensure SharePoint external sharing is managed through domain whitelist/blacklists | In SharePoint Admin Center > External Sharing, configure whitelists/blacklists to limit external sharing to approved domains. |
| 6.2 (L2) Block OneDrive for Business sync from unmanaged devices | In OneDrive Admin Center > Sync, configure the policy to block OneDrive sync on unmanaged devices, ensuring only secure devices can access data. |
| 6.3 (L1) Ensure expiration time for external sharing links is set | In SharePoint and OneDrive Admin Centers, set policies to enforce an expiration date on externally shared links to prevent perpetual access. |
| 6.4 (L2) Ensure ‘third-party storage services’ are restricted in ‘Microsoft 365 on the web’ | In Microsoft 365 Admin Center, configure settings to block or restrict access to third-party storage services in Office Online (e.g., Google Drive). |
| 6.5 (L2) Ensure additional storage providers are restricted in Outlook on the web | In Exchange Admin Center, configure policies that block access to additional third-party storage providers within Outlook on the web. |
CIS (Mobile Device Management – MDM)
| Requirement | How to Implement |
|---|---|
| 7.1 (L1) Ensure mobile device management policies are set to require advanced security configurations | In Microsoft Intune, create Mobile Device Management (MDM) policies that enforce advanced security settings like encryption, password complexity, and device compliance. |
| 7.2 (L1) Ensure that mobile device password reuse is prohibited | In Intune > Device Configuration Profiles, configure policies that prevent password reuse on managed mobile devices to reduce the risk of compromise. |
| 7.3 (L1) Ensure that mobile devices are set to never expire passwords | In Intune > Device Compliance, configure password settings to ensure that mobile device passwords do not expire, in line with security best practices. |
| 7.4 (L1) Ensure that users cannot connect from devices that are jailbroken or rooted | In Intune > Compliance Policies, enforce policies that block access from jailbroken or rooted devices to prevent security vulnerabilities. |
| 7.5 (L2) Ensure mobile devices are set to wipe on multiple sign-in failures to prevent brute force compromise | In Intune, configure device security policies that enforce a wipe after a specific number of failed sign-in attempts to prevent brute-force attacks. |
| 7.6 (L1) Ensure that mobile devices require a minimum password length to prevent brute force attacks | In Intune > Compliance Policies, enforce a minimum password length for mobile devices to ensure password strength and security. |
| 7.7 (L1) Ensure devices lock after a period of inactivity to prevent unauthorized access | In Intune > Device Compliance Policies, configure devices to lock after a short period of inactivity (e.g., 5 minutes) to minimize unauthorized access. |
| 7.8 (L1) Ensure that mobile device encryption is enabled to prevent unauthorized access to mobile data | In Intune > Device Configuration, ensure that Device Encryption is enabled to secure data on all managed mobile devices. |
| 7.9 (L1) Ensure that mobile devices require complex passwords (Type = Alphanumeric) | In Intune, configure compliance policies to require alphanumeric passwords on mobile devices to enhance password complexity and security. |
| 7.10 (L1) Ensure that mobile devices require complex passwords (Simple Passwords = Blocked) | In Intune > Device Configuration Profiles, block the use of simple passwords to ensure mobile devices meet complexity requirements. |
| 7.11 (L1) Ensure that devices connecting have antivirus and a local firewall enabled | In Intune > Compliance Policies, enforce policies that require antivirus software and a local firewall to be enabled on all mobile devices. |
| 7.12 (L2) Ensure mobile device management policies are required for email profiles | In Intune, enforce MDM policies for users accessing email via mobile devices to ensure secure email access. |
| 7.13 (L1) Ensure mobile devices require the use of a password | In Intune > Device Compliance, configure policies that require all mobile devices to be secured with a password, improving overall device security. |

